In the ever-escalating battle against cyber threats, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) have emerged as indispensable components of network security architectures. While often mentioned in tandem, these systems serve distinct yet complementary purposes, enhancing the robustness of network defenses. This article delves into the advanced methods of network protection offered by IDS/IPS systems, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and addressing frequently asked questions (FAQs).
1. Understanding IDS and IPS: Core Differences
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS):
- Primary Function: Detection of potential security threats in real-time.
- Operation: Monitors network traffic for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activities, alerting administrators.
- Action: Typically does not alter network traffic; focuses on notification and logging.
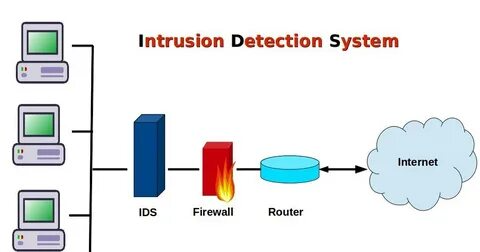
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS):
- Primary Function: Prevention of detected security threats.
- Operation: Not only identifies potential threats but also takes proactive measures to block or mitigate them.
- Action: Can drop packets, close connections, or alter traffic to prevent attacks.
2. Advanced Methods of Network Protection by IDS/IPS Systems
- *Anomaly-Based Detection: Identifies unusual patterns of network traffic that may indicate unknown threats.
- *Signature-Based Detection: Matches network traffic against a database of known threat signatures.
- *Stateful Inspection: Examines traffic in the context of the network’s state, enhancing detection accuracy.
- *Behavioral Analysis: Monitors system and user behavior to identify potential security threats.
- *Integration with Other Security Tools: Enhances overall security posture through seamless integration with firewalls, VPNs, and more.
3. Benefits of Implementing IDS/IPS Systems
- *Enhanced Security Posture: Proactive protection against known and unknown threats.
- *Real-Time Threat Detection and Prevention: Minimizes the window of vulnerability.
- *Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Supports meeting various industry security standards.
- *Forensic Analysis and Reporting: Provides detailed insights for post-incident analysis.
4. Best Practices for Effective IDS/IPS Deployment
- *Strategic Placement: Position IDS/IPS at network chokepoints for optimal visibility.
- *Regular Signature Updates: Ensure the system stays effective against new threats.
- *Customizable Alerting: Tailor notifications to reduce false positives and prioritize critical threats.
- *Continuous Monitoring and Analysis: Regularly review system logs and analytics for improved security insights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
While highly effective, no system can guarantee 100% protection. IDS/IPS are part of a layered security approach.
IPS typically requires more resources due to its proactive prevention mechanisms.
Yes, advanced evasion techniques can potentially bypass detection. Regular updates and advanced detection methods (e.g., behavioral analysis) help mitigate this risk.
Yes, many IDS/IPS solutions are designed for or can be adapted to cloud infrastructure, offering scalable security.
Conclusion
IDS and IPS systems represent a crucial frontline in the defense against cyber threats, offering advanced methods for network protection. By understanding their functionalities, benefits, and best practices for deployment, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, safeguarding against the evolving landscape of cyber attacks.

